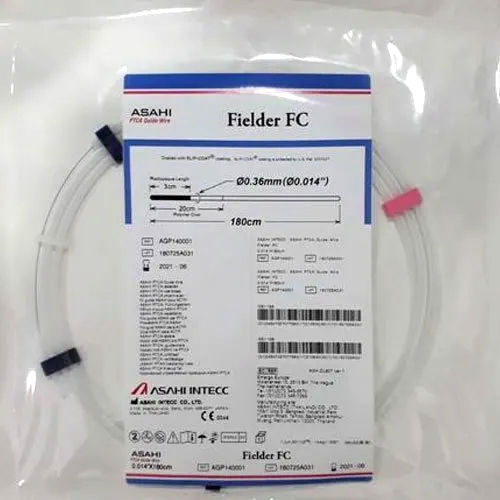
Asahi Fielder FC Guide Wire
Product Details:
- Equipment Type Guide Wire
- Use Medical
- Condition New
- Size Standard
- Portable Yes
- Warranty 1 Year
- Click to View more
Asahi Fielder FC Guide Wire Price And Quantity
- 50 Piece
- 3800 INR/Piece
Asahi Fielder FC Guide Wire Product Specifications
- 1 Year
- Standard
- Yes
- New
- Medical
- Guide Wire
Asahi Fielder FC Guide Wire Trade Information
- 10000 Piece Per Week
- 4 Days
- Asia, Australia, Central America, North America, South America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Middle East, Africa
- All India
Product Description
Asahi Fielder FC Guide Wire plays important role in successful execution of stent placement, angioplasty and cardiac catheterization procedures. It also simplifies critical urological, vascular and neurological surgeries. It provides error free guidance to different medical accessories while accessing specific body part. Being flexible, this guide wire goes through small channels and narrow spaces to navigate through the heart. It has standard tip radiopacity and specific tip load rate. Asahi Fielder FC Guide Wire is available with slip coated surface over its polymer jacketed body.
Product details
|
Length |
180 cm |
|
Category |
Treatment |
|
Brand |
Asahi |
|
Material |
PTCA |
|
Disposables |
Yes |
|
Automation Grade |
Manual |
|
Packing Type |
Packet |
|
Usage/Application |
Hospital / Clinic |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: The Asahi Fielder FC guide wire is what, exactly?
A: Angioplasty and stent insertion are two interventional procedures that make use of the Asahi Fielder FC guide wire. It is a thin, flexible wire that is intended to go through blood vessels while supporting and directing other medical devices.
Q: What purpose does the Asahi Fielder FC guide wire serve?
A: The guide wire is designed to be used in a variety of peripheral and cardiovascular procedures, such as accessing and navigating blood vessels, spanning lesions, and swapping out catheters or other devices.
Q: What distinguishes the Asahi Fielder FC guide wire from other types of guide wires?
A: The Asahi Fielder FC guide wire is renowned for its superior torque control, which makes navigation accurate and effective. Its hydrophilic coating improves trackability and decreases friction as it moves forward. Better steerability is made possible by the distal tip's flexibility, particularly in complex anatomies. It differs from other guide wires on the market because of the combination of these properties.
Q: Are there several sizes of the Asahi Fielder FC guide wire available?
A: To address varying patient anatomy and clinical demands, the Asahi Fielder FC guide wire is offered in a range of lengths and diameters. A healthcare provider can be consulted to discover the precise sizes, or you can look up the measurements in the manufacturer's specs.
Q: Does utilising the Asahi Fielder FC guide wire come with any potential hazards or complications?
A: Guide wire use carries possible dangers and problems, just like any other medical procedure. Vascular damage, perforation, dissection, thrombosis, embolism, infection, and allergic reactions to the device's components are a few examples. Before employing the guide wire, healthcare practitioners must carefully consider the unique circumstances, potential hazards, and advantages of each patient.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+